The world has entered an era of increasing instability as countries around the globe boost military spending in response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the Hamas attack on Israel, and China’s growing assertiveness in the South China Sea.
That was the conclusion of a new report released on February 13 by the International Institute for Strategic Studies, which also highlighted rising tensions in the Arctic, North Korea’s pursuit of nuclear weapons and the rise of military regimes in the Sahel region of Africa as contributing to a “deteriorating security environment.” The London-based think tank has compiled its annual estimate of the global military situation for 65 years.
“The current military-security situation heralds what is likely to be a more dangerous decade, characterized by the brazen application by some of military power to pursue claims — evoking a ‘might is right’ approach — as well as the desire among like-minded democracies for stronger bilateral and multilateral defense ties in response,” the report said.
Global defense spending rose 9% to $2.2 trillion last year as Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine, now entering its third year, heightened concerns that China and other militarily powerful states may try to impose their will on neighbors, the IISS said.
The increase was even steeper in NATO, which has supported Ukraine as a bulwark against further Russian incursions into Europe. The alliance’s non-U.S. members have boosted military spending by 32% since Russia invaded Ukraine’s Crimean peninsula in 2014, the institute found. Ten European members reached the alliance’s goal of spending 2% of economic output on defense last year, up from just two in 2014.
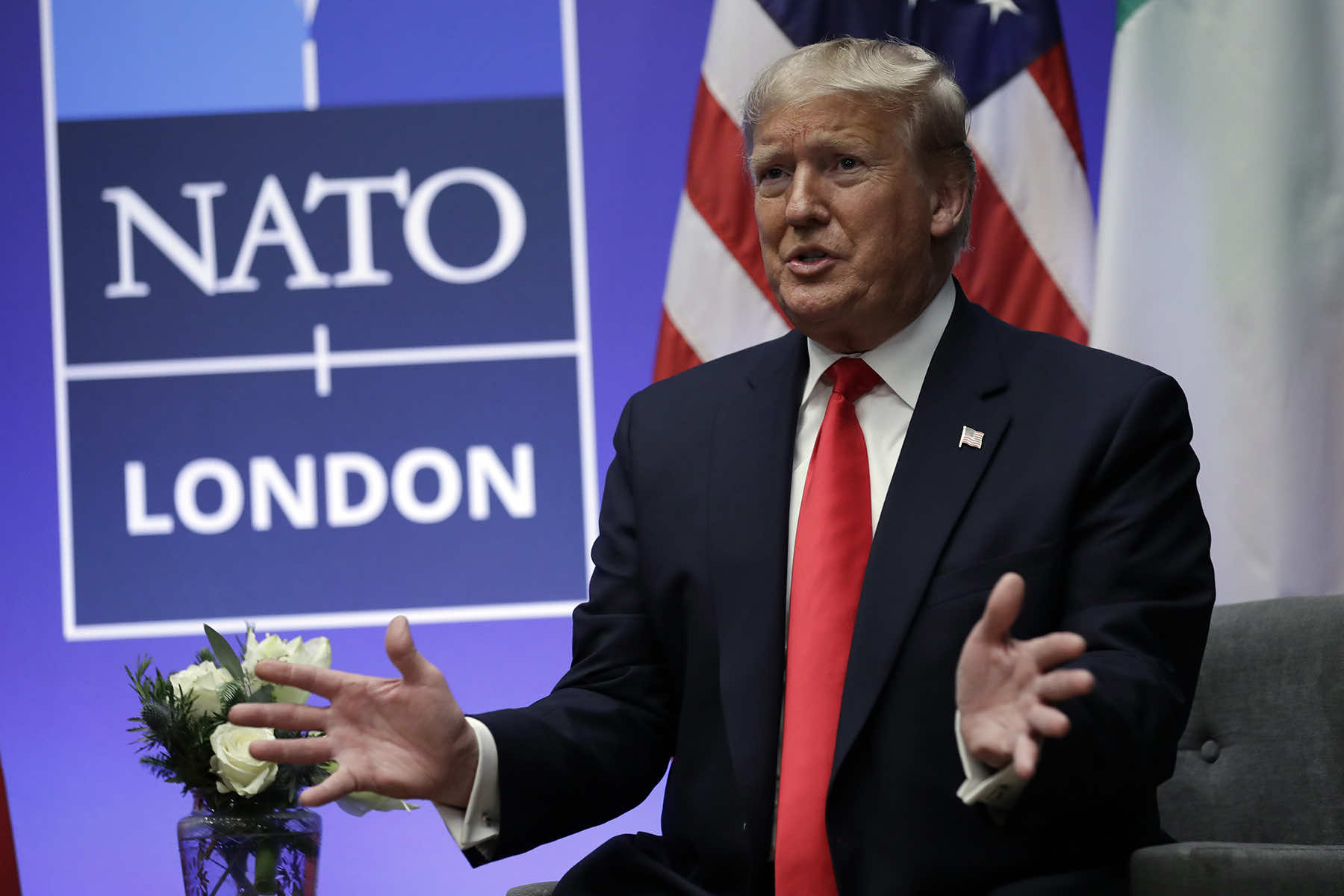
European defense spending received renewed attention in recent days after former U.S. President Donald Trump told a campaign rally that when he was president he told an unidentified NATO state he would “encourage” Russia to attack alliance members that didn’t meet their funding commitments.
“‘You didn’t pay? You’re delinquent?'” Trump recounted himself as saying. “‘No I would not protect you. In fact, I would encourage them to do whatever the hell they want. You gotta pay. You gotta pay your bills.'”
Trump’s remarks caused concern among alliance members such as Poland, where anxieties are high over the war Russia is waging in neighboring Ukraine. They also added to uneasiness over delays in the U.S. Congress’ passage of a $60 billion aid package for Ukraine.
Ben Barry, a senior fellow in land warfare at the institute, said Congress’ failure to approve the aid would likely embolden Russia to adopt a strategy of grinding away at Ukraine’s defenses and inflicting mass casualties.
The question for Ukraine’s allies “is, do they really want Ukraine to win?” Barry told reporters. “If they really want Ukraine to win, then they … need to double the amount of aid they’ve given last year, because the opportunity costs to Europe of a Russian victory are probably, in financial terms, even greater than the cost of, say, doubling down in their aid.”
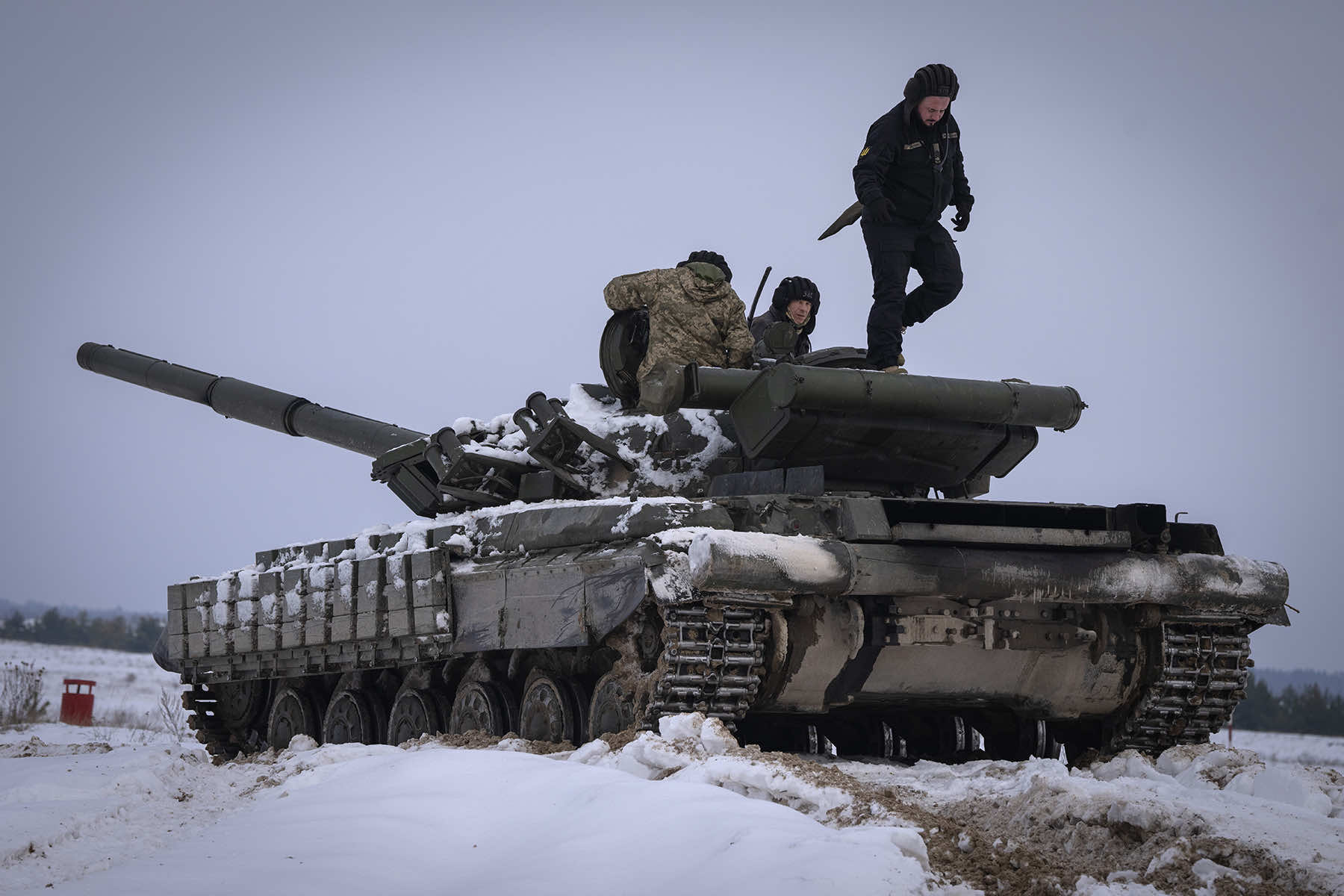
One of the report’s key findings is that Russia has lost some 3,000 main battle tanks during the fighting in Ukraine, or roughly as many as Moscow had in its active inventory before the full-scale invasion began in February 2022.
While Russia has replenished its forces by pulling 2,000 older tanks out of storage, the Ukrainian government in Kyiv is relying on Western nations to provide the ammunition and weaponry it needs to hold off its bigger neighbor.
“But Kyiv also continued to demonstrate its ingenuity in other ways, using Western and indigenously developed systems to put Russia’s Black Sea Fleet on the back foot,” the think tank said, citing Ukraine’s use of unmanned “maritime vehicles.”
Lessons learned from the war in Ukraine are starting to influence military planning in other countries, the IISS said. In particular, many countries have recognized that they need to increase production of military hardware and build up bigger stockpiles of material in case they are forced to fight a protracted war.
“A just-in-time mindset that has persisted for almost three decades is giving way to a just-in-case approach, though delivering on these ambitions is challenging,” the report said.