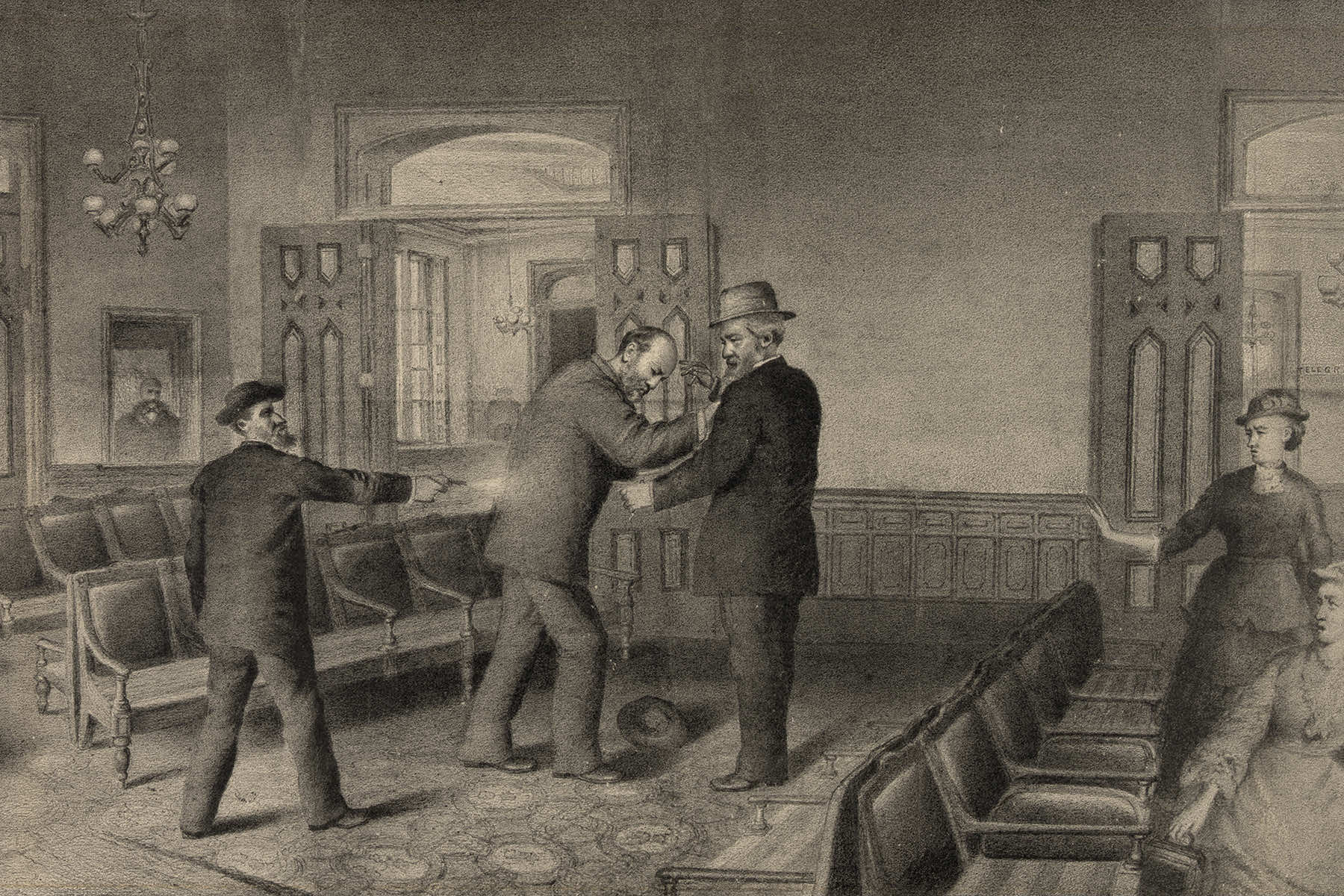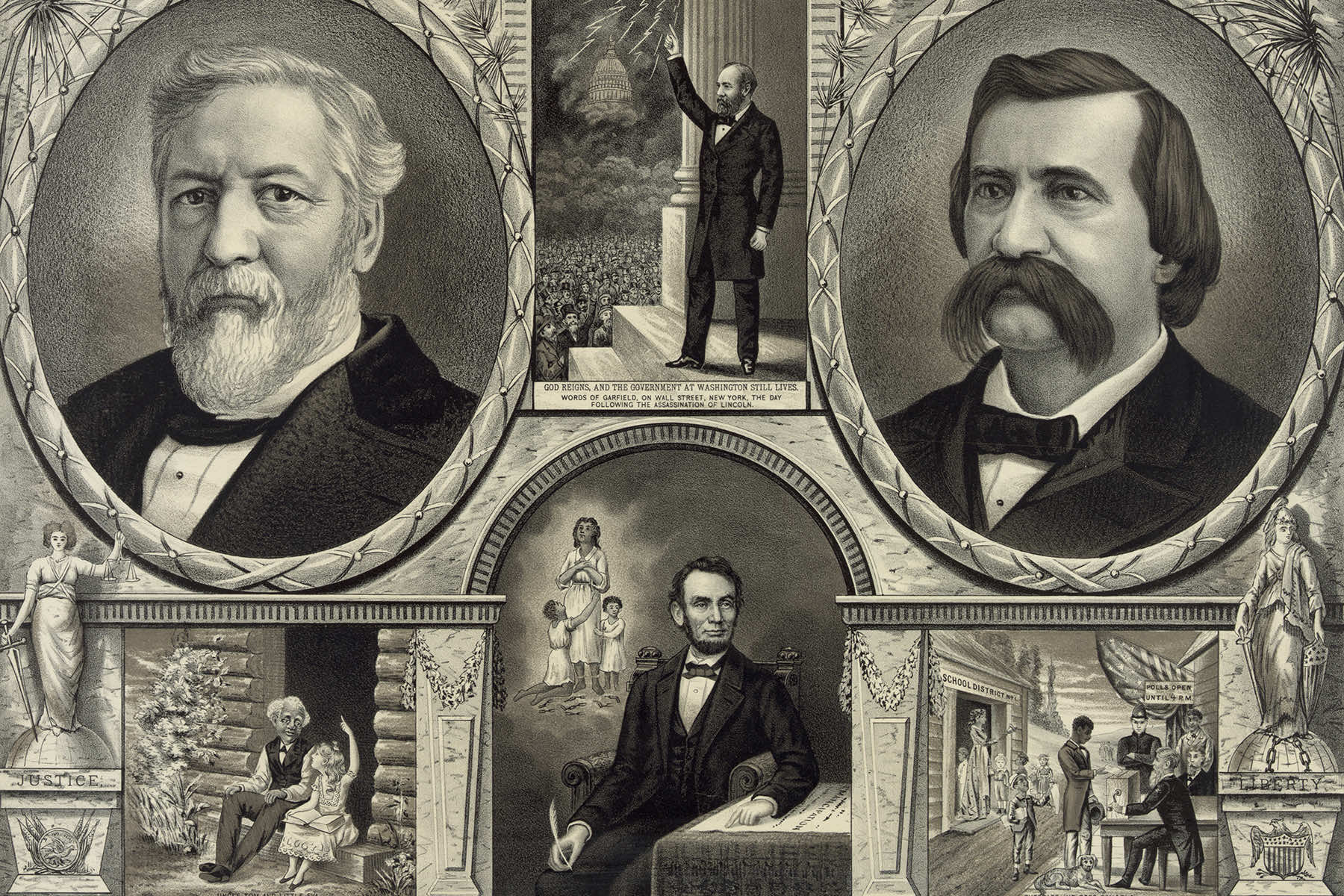
On August 6, 1880, Republican presidential candidate James A. Garfield gave one of his most famous speeches. Then a congressional representative from Ohio, Garfield was in New York City to make peace with Roscoe Conkling, a Republican kingmaker who hated him and his insistence on clean government.
In the evening, Garfield spoke to a crowd of well-wishers, made up in large part of men who had fought in the Civil War, as Garfield had. The one-time college professor spoke directly to the “Boys in Blue,” telling them “how great a thing it is to live in this Union and be a part of it.” He told them that they, the soldiers of the Civil War, represented the same ideas of union embraced by the men who framed the Constitution.
“Gentlemen,” said Garfield to great applause, “ideas outlive men; ideas outlive all earthly things. You who fought in the war for the Union fought for immortal ideas, and by their might you crowned the war with victory.
But victory was worth nothing except for the truths that were under it, in it, and above it. We meet to-night as comrades to stand guard around the sacred truths for which we fought. And while we have life to meet and grasp the hand of a comrade, we will stand by the great truths of the war.”
In 1880, four years after unreconstructed southern Democrats had taken control of all the former Confederate states and cemented the process of taking the vote away from Black men, Garfield promised that “we will remember our allies who fought with us.” He explained: “Soon after the great struggle began, we looked behind the army of White rebels, and saw 4,000,000 of Black people condemned to toil as slaves for our enemies; and we found that the hearts of these 4,000,000 were God-inspired with the spirit of liberty, and that they were all our friends.”
As the crowd applauded, he continued: “We have seen White men betray the flag and fight to kill the Union; but in all that long, dreary war we never saw a traitor in a Black skin.” To great cheers, he went on: “Our comrades escaping from the starvation of prison, fleeing to our lines by the light of the North star, never feared to enter the Black man’s cabin and ask for bread.” “That’s so!” yelled a man in the crowd. “In all that period of suffering and danger, no Union soldier was ever betrayed by a Black man or woman.”
“[S]o long as we live we will stand by these Black allies,” Garfield said. “We will stand by them until the sun of liberty, fixed in the firmament of our Constitution, shall shine with equal ray upon every man, Black or White, throughout the Union. Fellow-citizens, fellow-soldiers, in this there is the beneficence of eternal justice, and by it we will stand forever….” To wild cheers, Garfield concluded: “[T]he Republic rises on the glorious achievements of its dead and living heroes to a higher and nobler national life. We must stand guard over our past as soldiers, and over our country as the common heritage of all.”
In an era in which the smart money said the Democrats, with their promise to overturn the Reconstruction laws that established a legal framework for racial equality, would win the 1880 election, Garfield squeaked into the White House.
But he did not live long enough to put his vision into law. After his death, the Republican Party slid away from the protection of equal rights, focusing instead on protecting big business, its leaders looking the other way as state laws increasingly kept Black Americans and immigrants from voting so long as that same focus on state power prevented national regulation of business.
But those who believed in civil rights never gave up. In 1909 the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) organized “to promote equality of rights and eradicate caste or race prejudice among citizens of the United States,” and worked to secure “complete equality before the law,” including voting rights.
NAACP members publicized racial atrocities and insisted that authorities enforce the laws already on the books. By the 1960s, those protecting Black rights ramped up their efforts to register voters and to organize communities to support political change. When voter registration workers disappeared during the “Freedom Summer” of 1964, popular anger at their disappearance gave Democratic president Lyndon Baines Johnson leverage to pressure Congress to act. It passed the Civil Rights Act of 1964, in part to make it easier to vote.
After voters put Johnson back into the White House in November 1964, voting rights activists stepped up their efforts. In Selma, Alabama, where the voting rolls were 99% White even though Black Americans outnumbered White Americans, law enforcement officers harassed activists. After officers beat and shot an unarmed man marching for voting rights in a town near Selma, Black leaders planned a march from Selma to the state capitol at Montgomery to draw attention to voter suppression.
Law enforcement officers met the protesters on March 7, 1965, with billy clubs, bullwhips, and tear gas. On March 15, Johnson addressed a nationally televised joint session of Congress to ask it to pass a national voting rights act.
Our fathers believed that if [their] noble view of the rights of man was to flourish, it must be rooted in democracy,” he said. “The most basic right of all was the right to choose your own leaders. The history of this country, in large measure, is the history of the expansion of that right to all of our people.”
He submitted to Congress voting rights legislation, and Congress delivered. On August 6, 1965, Johnson signed the Voting Rights Act to guarantee Black Americans the right to vote.
“Today is a triumph for freedom as huge as any victory that has ever been won on any battlefield,” Johnson told the American people in a televised joint session of Congress. The Civil War had promised equality to all Americans, but that promise had not been fulfilled. “Today is a towering and certain mark that, in this generation, that promise will be kept.”
“I pledge you that we will not delay, or we will not hesitate, or we will not turn aside until Americans of every race and color and origin in this country have the same right as all others to share in the process of democracy,” Johnson said.
That resolve did not hold. In the 2013 Shelby County v. Holder decision, the Supreme Court significantly weakened the Voting Rights Act. Republican-dominated states immediately found ways to keep minority voters from the polls and their votes from being counted, and in 2020, then-president Trump tried to throw out the votes of people in majority Black districts in order to overturn the results of that year’s presidential election. On July 10, 2023, House Republicans introduced a sweeping “election integrity” bill that would loosen campaign finance regulations and make it harder to vote.
Eight days later, on July 18, Democrats in the House and Senate reintroduced the Freedom to Vote Act, which would make it easier for all Americans to vote, end partisan gerrymandering, require transparency in campaign donations to try to limit dark money in elections, and protect state and local election officials.
“The story of American democracy is one of a relentless march towards further equality,” said Senate majority leader Chuck Schumer (D-NY). “The Freedom To Vote Act would rectify one of the great historic harms of our past and put us closer to our goal of a fully representative democracy.”
And then, on August 1, the Department of Justice charged Trump under laws Congress passed during Reconstruction to protect the Black Americans’ political rights. Trump is charged with conspiring to obstruct an official proceeding — violating a law passed to stop Ku Klux Klan terrorists from breaking up official meetings in the late 1860s — and obstructing that proceeding: the counting of electoral votes.
Trump is also charged with conspiring “to injure, oppress, threaten, and intimidate one or more persons in the free exercise and enjoyment of a right and privilege secured to them by the Constitution and laws of the United States — that is, the right to vote, and to have one’s vote counted.”
Library of Congress
Letters from an Аmerican is a daily email newsletter written by Heather Cox Richardson, about the history behind today’s politics