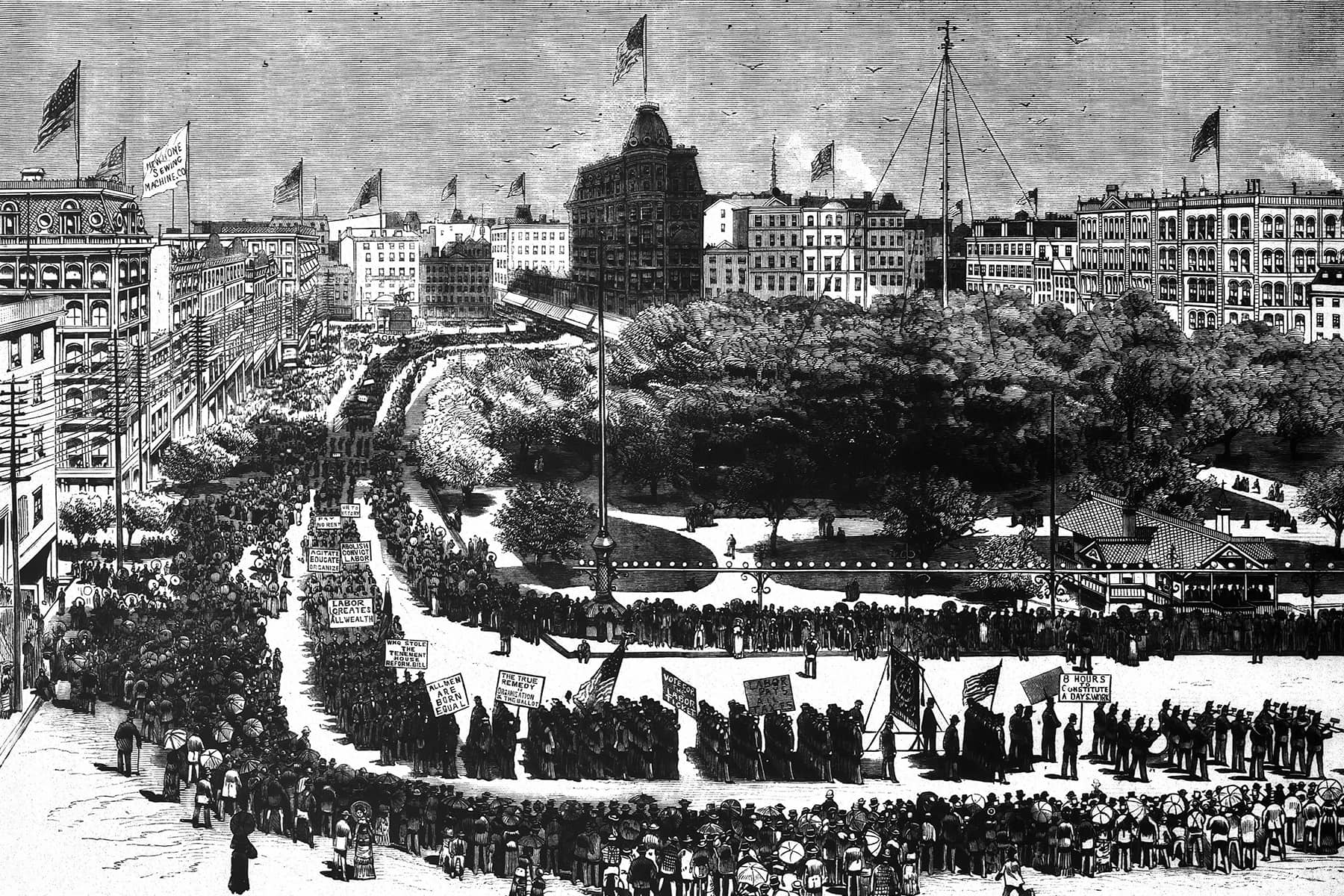
One hundred and forty years ago, on September 5, 1882, workers in New York City celebrated the first Labor Day holiday with a parade. The parade almost did not happen: there was no band, and no one wanted to start marching without music.
Once the Jewelers Union of Newark Two showed up with musicians, the rest of the marchers, eventually numbering between 10,000 and 20,000 men and women, fell in behind them to parade through lower Manhattan. At noon, when they reached the end of the route, the march broke up and the participants listened to speeches, drank beer, and had picnics. Other workers joined them.
Their goal was to emphasize the importance of workers in the industrializing economy and to warn politicians that they could not be ignored. Less than 20 years before, northern men had fought a war to defend a society based on free labor and had, they thought, put in place a government that would support the ability of all hardworking men to rise to prosperity.
By 1882, though, factories and the fortunes they created had swung the government toward men of capital, and workingmen worried they would lose their rights if they didn’t work together. A decade before, the Republican Party, which had formed to protect free labor, had thrown its weight behind Wall Street. By the 1880s, even the staunchly Republican Chicago Tribune complained about the links between business and government: “Behind every one of half of the portly and well-dressed members of the Senate can be seen the outlines of some corporation interested in getting or preventing legislation,” it wrote. The Senate, Harper’s Weekly noted, was “a club of rich men.”
The workers marching in New York City carried banners saying: “Labor Built This Republic and Labor Shall Rule it,” “Labor Creates All Wealth,” “No Land Monopoly,” “No Money Monopoly,” “Labor Pays All Taxes,” “The Laborer Must Receive and Enjoy the Full Fruit of His Labor,” ‘Eight Hours for a Legal Day’s Work,” and “The True Remedy is Organization and the Ballot.”
The New York Times denied that workers were any special class in the United States, saying that “[e]very one who works with his brain, who applies accumulated capital to industry, who directs or facilitates the operations of industry and the exchange of its products, is just as truly a laboring man as he who toils with his hands…and each contributes to the creation of wealth and the payment of taxes and is entitled to a share in the fruits of labor in proportion to the value of his service in the production of net results.”
In other words, the growing inequality in the country was a function of the greater value of bosses than their workers, and the government could not possibly adjust that equation. The New York Daily Tribune scolded the workers for holding a political—even a “demagogical”—event. “It is one thing to organize a large force of…workingmen…when they are led to believe that the demonstration is purely non-partisan; but quite another thing to lead them into a political organization….”
Two years later, workers helped to elect Democrat Grover Cleveland to the White House. A number of Republicans crossed over to support the reformer Cleveland, afraid that, as he said, “The gulf between employers and the employed is constantly widening, and classes are rapidly forming, one comprising the very rich and powerful, while in another are found the toiling poor…. Corporations, which should be the carefully restrained creatures of the law and the servants of the people, are fast becoming the people’s masters.”
In 1888, Cleveland again won the popular vote– by about 100,000 votes– but his Republican opponent, Benjamin Harrison, won in the Electoral College. Harrison promised that his would be “A BUSINESS MAN’S ADMINISTRATION” and said that “before the close of the present Administration business men will be thoroughly well content with it….”
Businessmen mostly were, but the rest of the country wasn’t. In November 1892 a Democratic landslide put Cleveland back in office, along with the first Democratic Congress since before the Civil War. As soon as the results of the election became apparent, the Republicans declared that the economy would collapse. Harrison’s administration had been “beyond question the best business administration the country has ever seen,” one businessmen’s club insisted, so losing it could only be a calamity. “The Republicans will be passive spectators,” the Chicago Tribune noted. “It will not be their funeral.” People would be thrown out of work, but “[p]erhaps the working classes of the country need such a lesson….”
As investors rushed to take their money out of the U.S. stock market, the economy collapsed a few days before Cleveland took office in early March 1893. Trying to stabilize the economy by enacting the proposals capitalists wanted, Cleveland and the Democratic Congress had to abandon many of the pro-worker policies they had promised, and the Supreme Court struck down the rest (including the income tax).
They could, though, support Labor Day and its indication of workers’ political power. On June 28, 1894, Cleveland signed Congress’s bill making Labor Day a legal holiday.
In Chicago the chair of the House Labor Committee, Lawrence McGann (D-IL), told the crowd gathered for the first official observance: “Let us each Labor day, hold a congress and formulate propositions for the amelioration of the people. Send them to your Representatives with your earnest, intelligent indorsement [sic], and the laws will be changed.”
Library of Congress and the Еvеrеtt Collection
Letters from an Аmerican is a daily email newsletter written by Heather Cox Richardson, about the history behind today’s politics