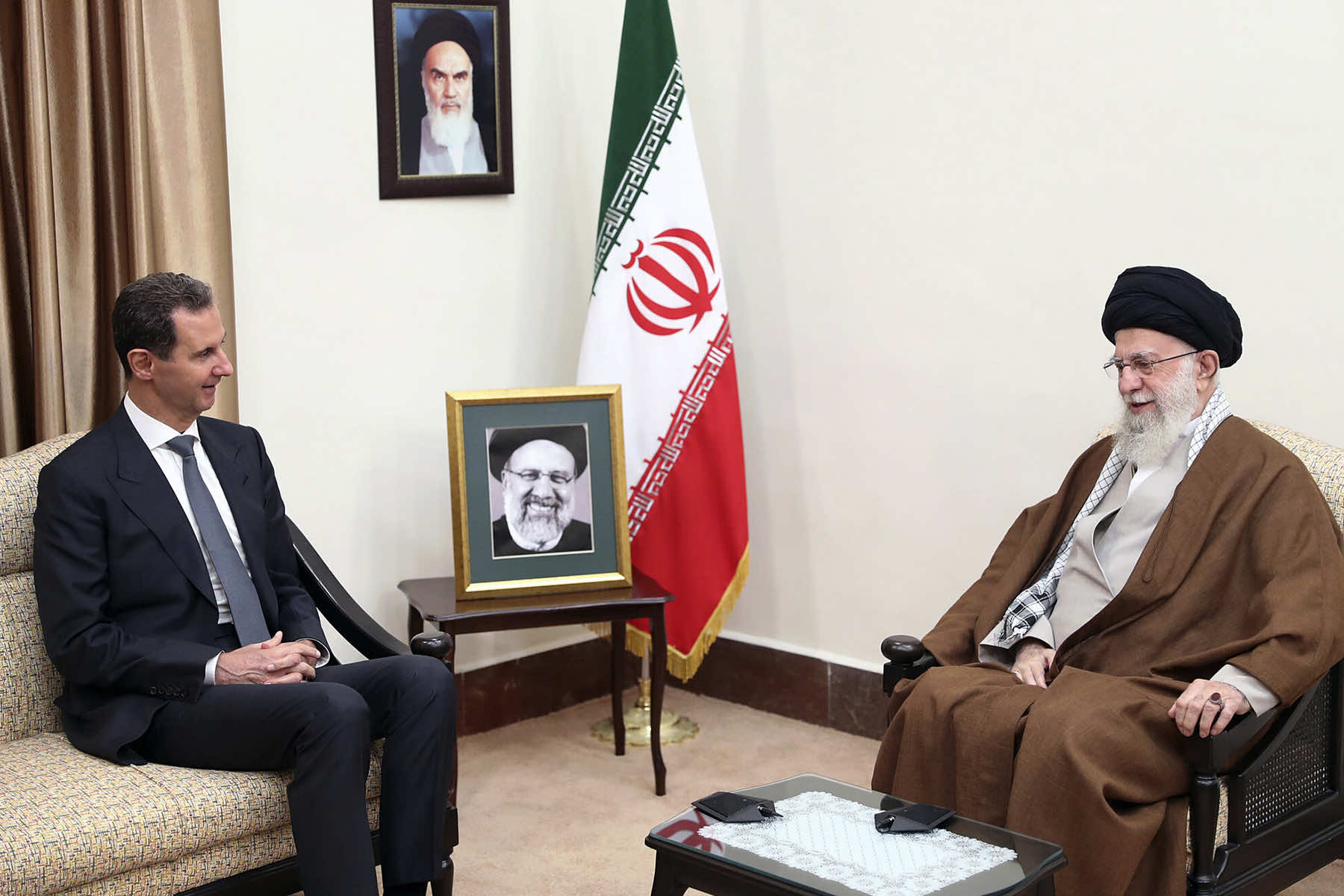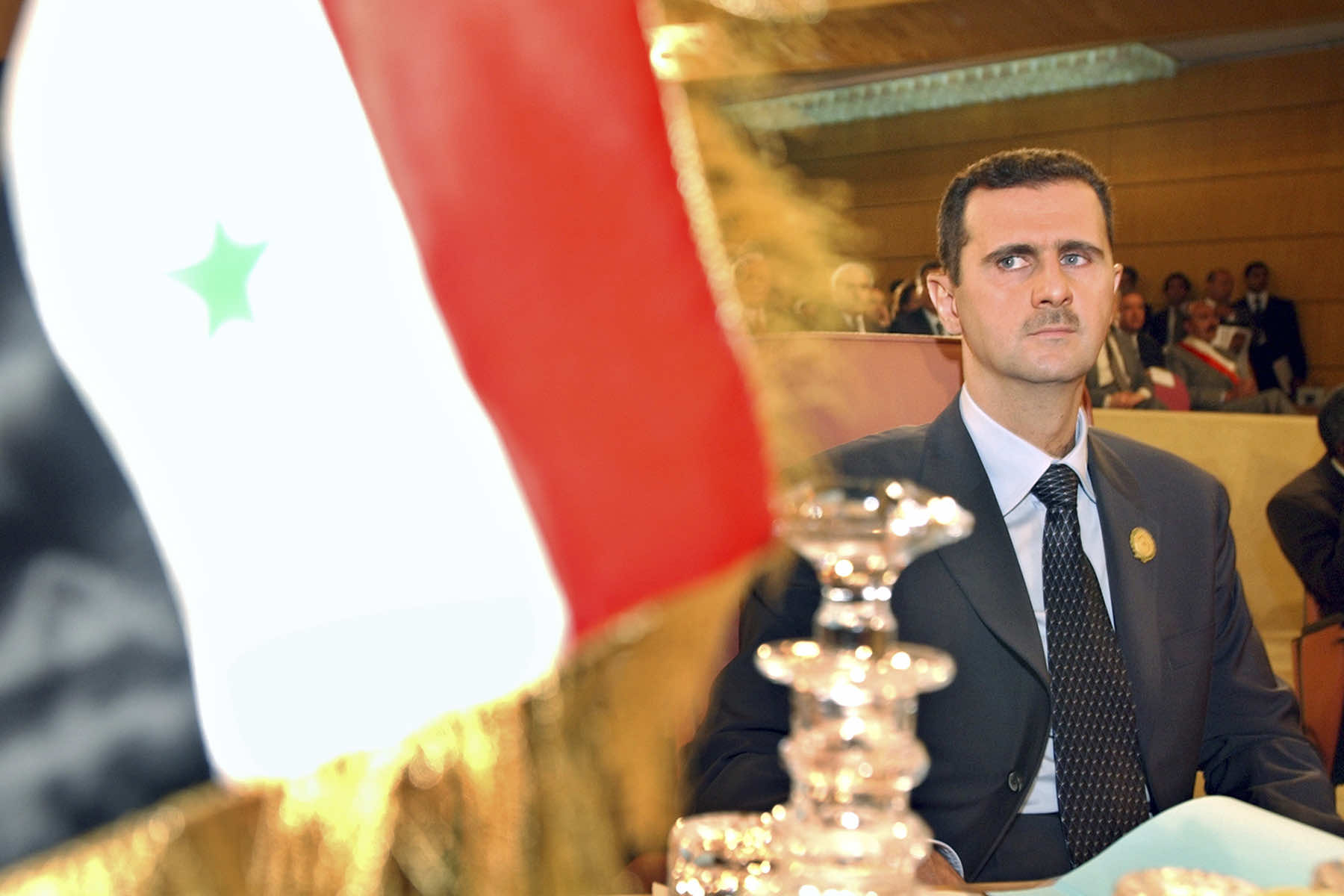
Syrian President Bashar Assad fled the country on December 8, bringing to a dramatic close his nearly 14-year struggle to hold onto control as his country fragmented in a brutal civil war that became a proxy battlefield for regional and international powers.
Assad’s exit stood in stark contrast to his first months as Syria’s unlikely president in 2000, when many hoped he would be a young reformer after three decades of his father’s iron grip. Only 34 years old, the Western-educated ophthalmologist appeared as a geeky tech-savvy fan of computers with a gentle demeanor.
But when faced with protests against his rule that erupted in March 2011, Assad turned to the brutal tactics of his father in an attempt to crush dissent. As the uprising hemorrhaged into an outright civil war, he unleashed his military to blast opposition-held cities, with support from allies Iran and Russia.
International rights groups and prosecutors alleged widespread use of torture and extrajudicial killings in Syria’s government-run detention centers. The war has killed nearly half a million people and displaced half of the country’s prewar population of 23 million.
The conflict appeared to be frozen in recent years, with Assad’s government regaining control of most of Syria’s territory while the northwest remained under the control of opposition groups and the northeast under Kurdish control.
Although Damascus remained under crippling Western sanctions, neighboring countries had begun to resign themselves to Assad’s continued hold on power. The Arab League reinstated Syria’s membership last year, and Saudi Arabia in May announced the appointment of its first ambassador since severing ties with Damascus 12 years ago.
However, the geopolitical tide turned quickly when opposition groups in northwest Syria in late November launched a surprise offensive. Government forces quickly collapsed while Assad’s allies, preoccupied by other conflicts — Russia’s war in Ukraine and the yearlong wars between Israel and the Iran-backed militant groups Hezbollah and Hamas — appeared reluctant to forcefully intervene.
AN END TO DECADES OF FAMILY RULE
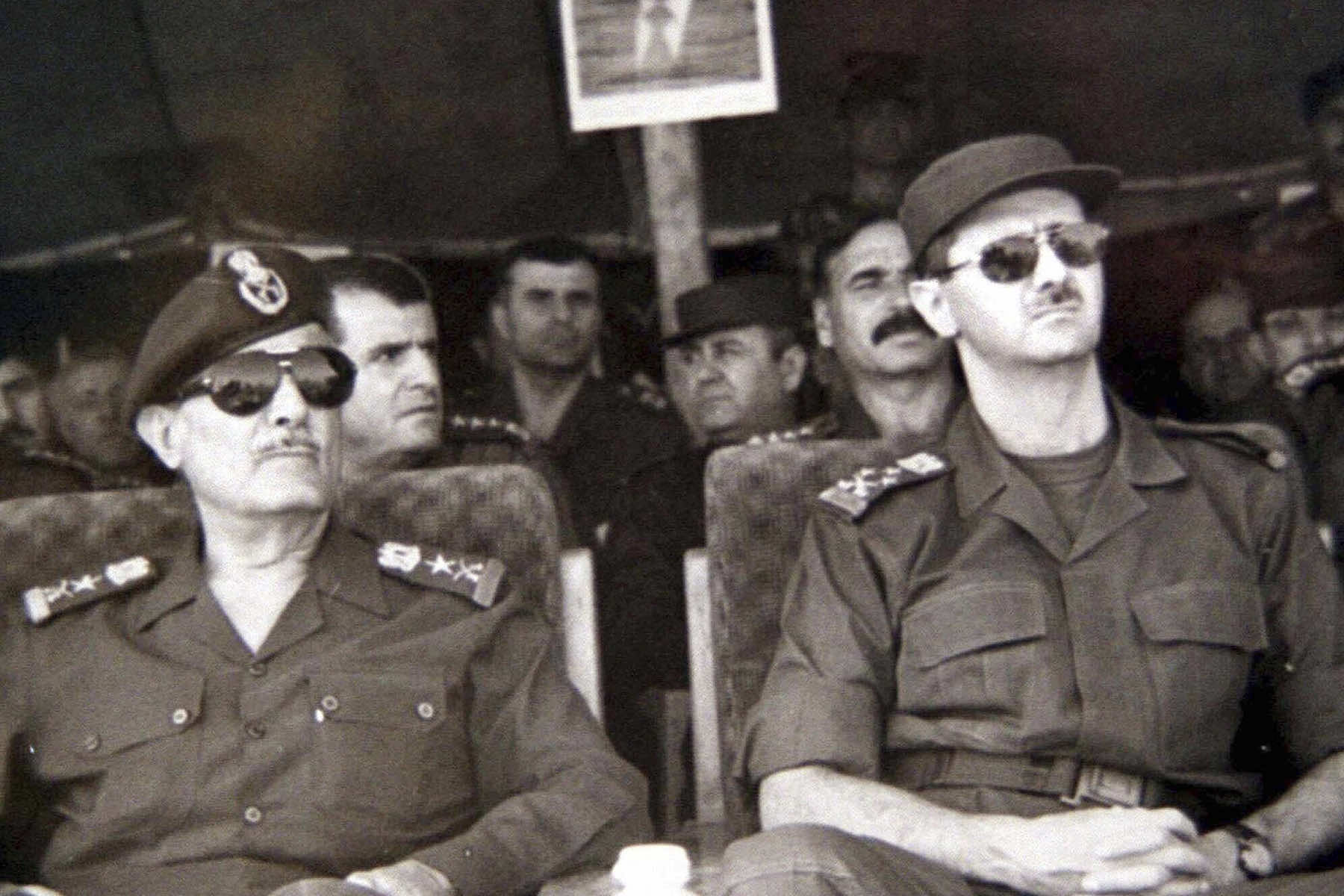
Assad came to power in 2000 by a twist of fate. His father had been cultivating Bashar’s oldest brother, Basil, as his successor, but in 1994, Basil was killed in a car crash in Damascus. Bashar was brought home from his ophthalmology practice in London, put through military training and elevated to the rank of colonel to establish his credentials so he could one day rule.
When Hafez Assad died in 2000, parliament quickly lowered the presidential age requirement from 40 to 34. Bashar’s elevation was sealed by a nationwide referendum, in which he was the only candidate.
Hafez, a lifelong military man, ruled the country for nearly 30 years during which he set up a Soviet-style centralized economy and kept such a stifling hand over dissent that Syrians feared even to joke about politics to their friends.
He pursued a secular ideology that sought to bury sectarian differences under Arab nationalism and the image of heroic resistance to Israel. He formed an alliance with the Shiite clerical leadership in Iran, sealed Syrian domination over Lebanon and set up a network of Palestinian and Lebanese militant groups. Bashar initially seemed completely unlike his strongman father.
Tall and lanky with a slight lisp, he had a quiet, gentle demeanor. His only official position before becoming president was head of the Syrian Computer Society. His wife, Asma al-Akhras, whom he married several months after taking office, was attractive, stylish and British-born.
The young couple, who eventually had three children, seemed to shun trappings of power. They lived in an apartment in the upscale Abu Rummaneh district of Damascus, as opposed to a palatial mansion like other Arab leaders.
Initially upon coming to office, Assad freed political prisoners and allowed more open discourse. In the “Damascus Spring,” salons for intellectuals emerged where Syrians could discuss art, culture and politics to a degree impossible under his father.
But after 1,000 intellectuals signed a public petition calling for multiparty democracy and greater freedoms in 2001, and others tried to form a political party, the salons were snuffed out by the feared secret police, who jailed dozens of activists.
TESTED BY THE ARAB SPRING, ASSAD RELIED ON OLD ALLIANCES TO STAY IN POWER
Instead of a political opening, Assad turned to economic reforms. He slowly lifted economic restrictions, let in foreign banks, threw the doors open to imports and empowered the private sector. Damascus and other cities long mired in drabness saw a flourishing of shopping malls, new restaurants and consumer goods. Tourism swelled.
Abroad, he stuck to the line his father had set, based on the alliance with Iran and a policy of insisting on a full return of the Israel-annexed Golan Heights, although in practice Assad never militarily confronted Israel.
In 2005, he suffered a heavy blow with the loss of Syria’s decades-old control over neighboring Lebanon after the assassination of former Prime Minister Rafik Hariri. With many Lebanese accusing Damascus of being behind the slaying, Syria was forced to withdraw its troops from the country and a pro-American government came to power.
At the same time, the Arab world split into two camps — one of U.S.-allied, Sunni-led countries such as Saudi Arabia and Egypt, the other Syria and Shiite-led Iran with their ties to Hezbollah and Palestinian militants.
Throughout, Assad relied largely on the same power base at home as his father: his Alawite sect, an offshoot of Shiite Islam comprising around 10% of the population. Many of the positions in his government went to younger generations of the same families that had worked for his father. Drawn in as well were members of the new middle class created by his reforms, including prominent Sunni merchant families.
Assad also turned to his own family. His younger brother Maher headed the elite Presidential Guard and would lead the crackdown against the uprising. Their sister Bushra was a strong voice in his inner circle, along with her husband, Deputy Defense Minister Assef Shawkat, until he was killed in a 2012 bombing. Bashar’s cousin, Rami Makhlouf, became the country’s biggest businessman, heading a financial empire before the two had a falling-out that led to Makhlouf being pushed aside.
Assad also increasingly entrusted key roles to his wife, Asma, before she announced in May that she was undergoing treatment for leukemia and stepped out of the limelight.
When 2011 protests erupted in Tunisia and Egypt, eventually toppling their rulers, Assad dismissed the possibility of the same occurring in his country, insisting his regime was more in tune with its people. After the Arab Spring wave reached Syria, his security forces staged a brutal crackdown while Assad consistently denied he was facing a popular revolt. He instead blamed “foreign-backed terrorists” trying to destabilize his regime.
His rhetoric struck a chord with many in Syria’s minority groups — including Christians, Druze, and Shiites — as well as some Sunnis who feared the prospect of rule by Sunni extremists even more than they disliked Assad’s authoritarian rule.
As the uprising spiraled into a civil war, millions of Syrians fled to Jordan, Turkey, Iraq, and Lebanon, and on to Europe.
Ironically, on February 26, 2011, two days after the fall of Egypt’s Hosni Mubarak to protesters and just days before the wave of Arab Spring protests swept into his country, Assad e-mailed a joke he had run across mocking the Egyptian leader’s stubborn refusal to step down.





















